Digital manufacturing is reshaping how products are designed, validated, and built. Additive manufacturing is now a production-ready pathway for lighter, stronger parts and rapid iteration. To capitalize on this shift, teams need a CAD platform that keeps the digital thread intact from concept to print to post-processing. That’s where PTC Creo shines.
Digital Manufacturing and Additive Manufacturing
Digital manufacturing uses connected, software-driven workflows to improve quality and efficiency while reducing time and waste. This includes CAD, simulation, CAM, PLM, and analytics. A strong digital thread means changes propagate automatically across design, simulation, manufacturing, and service documentation.
Additive manufacturing (AM) builds parts layer by layer directly from CAD. Unlike traditional prototyping alone, modern AM supports full-scale production with design freedoms that machining or casting can’t match. This includes lightweight lattices, organic geometries, and single-piece part consolidation.
Together, digital and additive manufacturing let teams iterate faster, validate earlier, and move to production with less risk.
Creo’s Digital & Additive Manufacturing Capabilities
Creo offers many digital and additive manufacturing features that make designing easier.
Design for Additive: Lattices, Generative Concepts, and Simulation
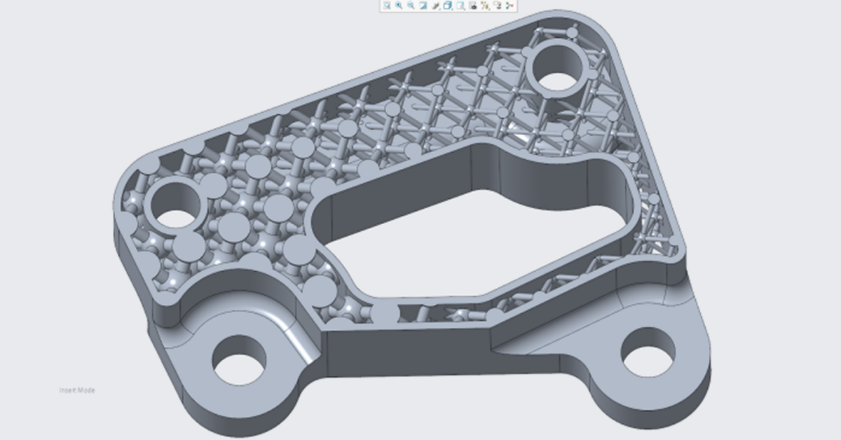
- Lattice features (AM Extension): Create robust, lightweight structures that save material and improve performance. Creo includes multiple lattice types (including formula-driven and stochastic), with fine control over cell size, beam thickness, and boundary regions. It enables designs that would otherwise be impossible with 3-axis machining.
- Self-supporting, formula-driven lattices: Especially useful for metal AM, these patterns minimize support needs and post-processing time.
- Generative design & live simulation: Explore many concepts quickly, optimize for weight/strength/stiffness, then validate with integrated analysis (stress, deformation, temperature). This tight loop reduces over-engineering and gets you to a printable, production-ready design faster.
Build Preparation Inside CAD
- Printer tray setup & nesting: Arrange parts manually or use nesting optimization for efficient packing, better throughput, and reduced waste. The result stays as a standard Creo assembly, fully associative to your design.
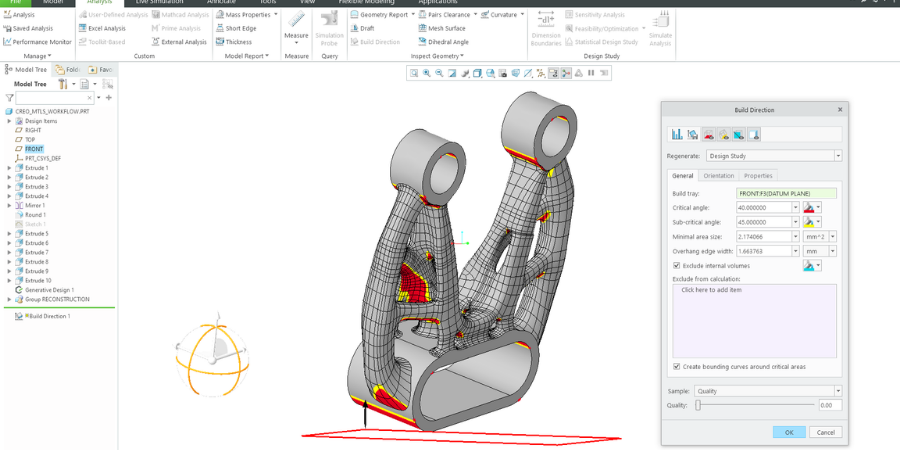
- Build direction analysis & orientation optimization: Automatically compute orientations that balance print speed, support volume, and surface quality. For complex geometries, Creo finds optimal orientations you might miss manually.
- Support structure generation (Advanced AM for Metal): Define support profiles with parameters for heat dissipation, easy removal, and minimal material. Supports remain associative, so if geometry or settings change, updates are painless.
Industrial File Formats & Rich Metadata
- 3MF export (standard AM Extension): Move beyond STL. 3MF carries materials, colors/appearances, and orientations so printers receive a more complete, reliable build instruction. Many teams adopt Creo’s AM Extension just for 3MF because it cuts downstream errors and setup time.
Direct Printer Connectivity & Job Management
- Materialize Magics/Build Processors (Advanced AM): Connect directly from Creo to a wide array of metal printers. You may also manage machines and review queued jobs without leaving CAD. For polymers, Creo supports direct interfaces with major OEMs, streamlining the handoff from engineering to the shop floor.
Slice Preview & Verification
- In-CAD slice visualization (e.g., CLI preview): Inspect layer-by-layer results before sending a job. Spot thin walls, islands, or overhang issues and adjust geometry, orientation, or supports immediately. This saves time, material, and reprints.
Part Consolidation & Hybrid Workflows
- Design once, finish smart: Print near-net shapes for complex parts, then finish critical features on 3- or 5-axis machines. This hybrid approach unlocks materials and geometries that don’t cast well while keeping tight tolerances where you need them.
- Part consolidation: Replace multi-part assemblies with a single printed component. You’ll cut fasteners, reduce assembly labor, and often improve durability all while maintaining traceability through the digital thread.
Digital Thread & Change Propagation
- Single source of truth: With Creo tied into PLM, any design change propagates to simulation, build setups, technical illustrations, and service content. That means fewer manual handoffs, fewer mismatches, and faster engineering change cycles.
Real-World Results of Digital and Additive Manufacturing in Creo
As seen above, there are many benefits of these features, but the following results are directly caused by these capabilities. Faster new part introduction is achieved through a design-to-print workflow in one environment. This environment leads to minimized context switching and reduced errors. Costs are also lowered as lattices cut material use, orientation and support optimization reduce scrap, and part consolidation shortens assembly time. In addition to this, quality improves with early, integrated simulation and in-CAD slice checks that catch issues before printing begins. Finally, scalability is supported through tray optimization, printer management, and associative support. It enables consistent, production-grade additive manufacturing.
Digital Manufacturing and Additive Manufacturing with Creo
Creo and 3D printing are built for production, not just prototypes. By unifying additive manufacturing in CAD, Creo delivers a complete digital manufacturing workflow. The result: lighter parts, fewer iterations, shorter lead times, and a resilient digital thread that keeps teams aligned from concept to shop floor. If you’re ready to anchor your workflow in digital manufacturing, Creo is a proven path forward. Contact us today to see how you can get started with Creo.